Localizing and classifing thoracic abnormalities from Chest Radiographs
Here we will create an object Detection Model, that automatically localizes and classifyies 14 types of thoracic abnormalities from chest radiographs. It is trained using pretrained faster_rcnn model from pytorch.
Dataset Information:
The dataset comprises 18,000 postero-anterior (PA) CXR scans in DICOM format, which were de-identified to protect patient privacy. All images were labeled by a panel of experienced radiologists for the presence of 14 critical radiographic findings as listed below:
- Dataset Source : vindr.ai
0 - Aortic enlargement
1 - Atelectasis
2 - Calcification
3 - Cardiomegaly
4 - Consolidation
5 - ILD
6 - Infiltration
7 - Lung Opacity
8 - Nodule/Mass
9 - Other lesion
10 - Pleural effusion
11 - Pleural thickening
12 - Pneumothorax
13 - Pulmonary fibrosis
14 - No Finding
Loading Useful libraries
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import pydicom
import time
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
import torch
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as T
from collections import defaultdict, deque
from torchvision.models.detection.faster_rcnn import FastRCNNPredictor
from torchvision.models.detection import FasterRCNN
from torchvision.models.detection.faster_rcnn import FastRCNNPredictor
from torchvision.models.detection import FasterRCNN
from torchvision.models.detection.rpn import AnchorGenerator
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset
from torch.utils.data.sampler import SequentialSampler
import cv2
import os,sys,matplotlib,re
from PIL import Image
from skimage import exposure
from pydicom.pixel_data_handlers.util import apply_voi_lut
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as immg
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
path = '../input/vinbigdata-resized-image-512/'
df = pd.read_csv('../input/vinbigdata-weighted-bbox-fusion/weighted_box_fused_train_vinBigData.csv')
df.head()
| image_id | class_id | rad_id | x_min | y_min | x_max | y_max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 50a418190bc3fb1ef1633bf9678929b3 | 14 | wbf | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 |
| 1 | 21a10246a5ec7af151081d0cd6d65dc9 | 14 | wbf | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 |
| 2 | 9a5094b2563a1ef3ff50dc5c7ff71345 | 3 | wbf | 690.666676 | 1354.333235 | 1658.666714 | 1797.666677 |
| 3 | 9a5094b2563a1ef3ff50dc5c7ff71345 | 0 | wbf | 1052.000000 | 715.000000 | 1299.000000 | 966.000000 |
| 4 | 9a5094b2563a1ef3ff50dc5c7ff71345 | 11 | wbf | 1789.000000 | 1729.000000 | 1875.000000 | 1992.000000 |
# replace NaN by 0
df = df.fillna(0)
img_dim = pd.read_csv('../input/vinbigdata-resized-image-512/train_meta.csv')
df = df.merge(img_dim,on='image_id',how='left')
Since Original Dataset has quite large images. I have here used resized images of size 512x512. So below we are simply rescaling bounding boxes according to new image sizes
df['x_min'] = df['x_min']*512/df['dim1']
df['x_max'] = np.ceil(df['x_max']*512/df['dim1'])
df['y_min'] = df['y_min']*512/df['dim0']
df['y_max'] = np.ceil(df['y_max']*512/df['dim0'])
df.describe()
| class_id | x_min | y_min | x_max | y_max | dim0 | dim1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 34510.000000 | 34510.000000 | 34510.000000 | 34510.000000 | 34510.000000 | 34510.000000 | 34510.000000 |
| mean | 9.320632 | 147.300599 | 132.937163 | 203.479252 | 179.701941 | 2838.098870 | 2493.697711 |
| std | 4.774856 | 138.360779 | 122.549886 | 168.006037 | 148.330784 | 292.973949 | 355.930804 |
| min | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 927.000000 | 823.000000 |
| 25% | 6.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 2615.000000 | 2304.000000 |
| 50% | 11.000000 | 121.470445 | 115.621184 | 202.000000 | 185.000000 | 2880.000000 | 2453.000000 |
| 75% | 14.000000 | 266.795256 | 229.463041 | 364.000000 | 311.000000 | 3072.000000 | 2742.000000 |
| max | 14.000000 | 496.250000 | 493.213918 | 512.000000 | 512.000000 | 3408.000000 | 3320.000000 |
df.columns
Index(['image_id', 'class_id', 'rad_id', 'x_min', 'y_min', 'x_max', 'y_max',
'dim0', 'dim1'],
dtype='object')
- Since class 14 is no findings we will simply remove them.
- Also since we are using faster RCNN, it has background as default class 0. So I am incrementing my classes by + 1
df = df[df['class_id']!=14]
df['class_id'] = df['class_id']+1
df = df.reset_index(drop=True)
df_grp = df.groupby(['image_id'])
b_fea = ['x_min', 'y_min', 'x_max', 'y_max']
import matplotlib
Sample Image
name = df.image_id.tolist()[85]
loc = '../input/vinbigdata-resized-image-512/train/'+name+'.png'
aaa = df_grp.get_group(name)
bbx = aaa.loc[:,b_fea]
img = immg.imread(loc)
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(18,10))
ax.imshow(img,cmap='binary')
for i in range(len(bbx)):
box = bbx.iloc[i].values
x,y,w,h = box[0], box[1], box[2]-box[0], box[3]-box[1]
rect = matplotlib.patches.Rectangle((x,y),w,h,linewidth=1,edgecolor='r',facecolor='none',)
ax.text(*box[:2], aaa['class_id'].iloc[i], verticalalignment='top', color='white', fontsize=15, weight='bold')
ax.add_patch(rect)
plt.show()
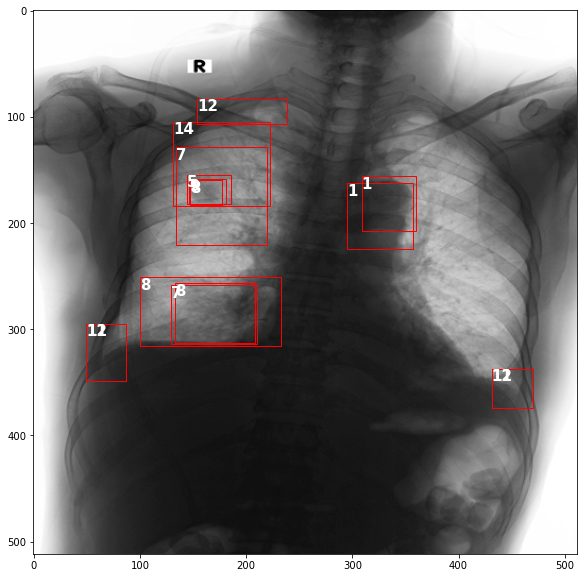
Dataset
img_dir = "../input/vinbigdata-resized-image-512/train/"
class XrayDataset(object):
def __init__(self, df, IMG_DIR, transforms=None):
# dataframe
self.df = df
#image directory
self.img_dir = IMG_DIR
#image transforms
self.transforms = transforms
#total unique images
self.image_ids = self.df['image_id'].unique().tolist()
def __len__(self):
return len(self.image_ids)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
#image id
image_id = self.image_ids[idx]
# taking bouding boxes and class concerning a unique image
records = self.df[self.df['image_id'] == image_id]
# read image
image = cv2.imread(self.img_dir+image_id+".png",cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB).astype(np.float32)
#normalize it
image /= 255.0
#bounding boxes
boxes = records[['x_min', 'y_min', 'x_max', 'y_max']].to_numpy()
# area of each bounding box
area = (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]) * (boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0])
# labels of each bounding box
labels = records['class_id'].tolist()
#target for faster rcnn
target = {}
target['boxes'] = boxes
target['labels'] = torch.tensor(labels)
target['image_id'] = torch.tensor([idx])
target['area'] = torch.as_tensor(area, dtype=torch.float32)
target['iscrowd'] = torch.zeros((records.shape[0],), dtype=torch.int64)
#transforms
if self.transforms:
sample = {
'image': image,
'bboxes': target['boxes'],
'labels': labels
}
sample = self.transforms(**sample)
image = sample['image']
target['boxes'] = torch.stack(tuple(map(torch.tensor, zip(*sample['bboxes'])))).permute(1, 0)
return torch.tensor(image), target, image_id
Since all images were in dicom format. Below function takes a dicom file and returns a image in numpy array
def read_xray(path, voi_lut = True, fix_monochrome = True):
dicom = pydicom.read_file(path)
# VOI LUT (if available by DICOM device) is used to transform raw DICOM data to "human-friendly" view
if voi_lut:
data = apply_voi_lut(dicom.pixel_array, dicom)
else:
data = dicom.pixel_array
# depending on this value, X-ray may look inverted - fix that:
if fix_monochrome and dicom.PhotometricInterpretation == "MONOCHROME1":
data = np.amax(data) - data
data = data - np.min(data)
data = data / np.max(data)
data = (data * 255).astype(np.uint8)
#img = cv2.resize(data,(512,512)).astype(np.float32)
return np.dstack((data,data,data))
Test Image Dir
ts_img_dir1 = '../input/vinbigdata-chest-xray-abnormalities-detection/test/'
ts_img_dir2 = '../input/vinbigdata-resized-image-512/test/'
Test Dataset
class TestDataset(object):
def __init__(self, df, IMG_DIR, transforms=None):
self.df = df
self.img_dir = IMG_DIR
self.transforms = transforms
self.image_ids = self.df['image_id'].tolist()
def __len__(self):
return len(self.image_ids)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
image_id = self.image_ids[idx]
#image = read_xray(ts_img_dir+image_id+".dicom")
image = cv2.imread(self.img_dir+image_id+".png",cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB).astype(np.float32)
# Test images won't need taregts
if self.transforms:
sample = {
'image': image,
}
sample = self.transforms(**sample)
image = sample['image']
return image, image_id,image.shape[1],image.shape[2]
Image Transforms
import albumentations as A
from albumentations.pytorch.transforms import ToTensorV2
def get_train_transform():
return A.Compose([
A.Flip(0.5),
ToTensorV2(p=1.0)
], bbox_params={'format': 'pascal_voc', 'label_fields': ['labels']})
def get_valid_transform():
return A.Compose([
ToTensorV2(p=1.0)
], bbox_params={'format': 'pascal_voc', 'label_fields': ['labels']})
def get_test_transform(IMG_SIZE=(512,512)):
return A.Compose([
A.Normalize(mean=(0, 0, 0), std=(1, 1, 1), max_pixel_value=255.0, p=1.0),
A.Resize(*IMG_SIZE),
ToTensorV2(p=1.0)
])
CDS = XrayDataset(df, img_dir ,get_train_transform())
Dataset Sample
import random
img, tar,_ = CDS[random.randint(0,1000)]
bbox = tar['boxes'].numpy()
labels = tar['labels'].numpy()
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(18,10))
ax.imshow(img.permute(1,2,0).cpu().numpy())
for i in range(len(bbox)):
box = bbox[i]
x,y,w,h = box[0], box[1], box[2]-box[0], box[3]-box[1]
rect = matplotlib.patches.Rectangle((x,y),w,h,linewidth=2,edgecolor='r',facecolor='none',)
ax.text(*box[:2], labels[0], verticalalignment='top', color='red', fontsize=13, weight='bold')
ax.add_patch(rect)
plt.show()
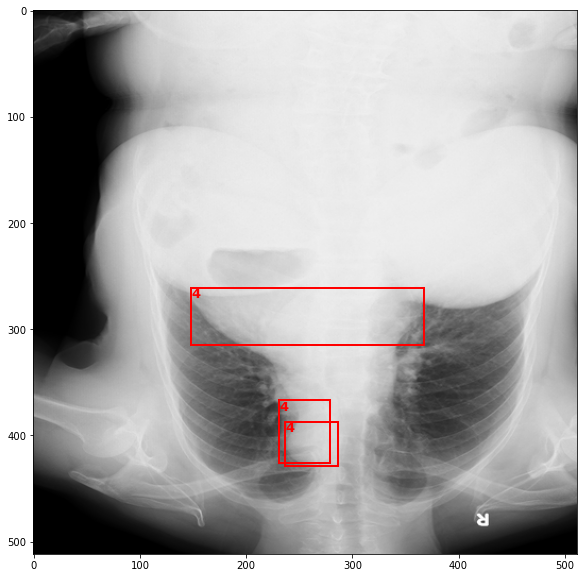
Splitting dataset between train and valid
image_ids = df['image_id'].unique()
train_ids = image_ids[:3075]
valid_ids = image_ids[3075:]
train_df = df[df['image_id'].isin(train_ids)]
valid_df = df[df['image_id'].isin(valid_ids)]
train_df.shape,valid_df.shape
((19101, 9), (4803, 9))
Dataloader for pytorch
def collate_fn(batch):
return tuple(zip(*batch))
train_dataset = XrayDataset(train_df,img_dir , get_train_transform())
valid_dataset = XrayDataset(valid_df,img_dir, get_valid_transform())
# split the dataset in train and test set
indices = torch.randperm(len(train_dataset)).tolist()
train_data_loader = DataLoader(
train_dataset,
batch_size=4,
shuffle=False,
num_workers=4,
collate_fn=collate_fn
)
valid_data_loader = DataLoader(
valid_dataset,
batch_size=4,
shuffle=False,
num_workers=4,
collate_fn=collate_fn
)
device = torch.device('cuda') if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.device('cpu')
Model Faster RCNN pretrained
num_classes = len(df['class_id'].unique())+1 # 1 class (wheat) + background
# load a model; pre-trained on COCO
model = torchvision.models.detection.fasterrcnn_resnet50_fpn(pretrained=True)
# get number of input features for the classifier
in_features = model.roi_heads.box_predictor.cls_score.in_features
# replace the pre-trained head with a new one
model.roi_heads.box_predictor = FastRCNNPredictor(in_features, num_classes)
Downloading: "https://download.pytorch.org/models/fasterrcnn_resnet50_fpn_coco-258fb6c6.pth" to /root/.cache/torch/hub/checkpoints/fasterrcnn_resnet50_fpn_coco-258fb6c6.pth
0%| | 0.00/160M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
model.to(device)
params = [p for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad]
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(params, lr=0.005, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.0005)
#Optimizers are algorithms or methods used to change the attributes of your neural network such as weights and learning rate in order to reduce the losses.
#How you should change your weights or learning rates of your neural network to reduce the losses is defined by the optimizers you use.
lr_scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=3, gamma=0.1)
#lr_scheduler = None
Averager just keep track of losses per epcoh
class Averager:
def __init__(self):
self.current_total = 0.0
self.iterations = 0.0
def send(self, value):
self.current_total += value
self.iterations += 1
@property
def value(self):
if self.iterations == 0:
return 0
else:
return 1.0 * self.current_total / self.iterations
def reset(self):
self.current_total = 0.0
self.iterations = 0.0
Training
num_epochs = 15 # Number of epoch to train
loss_hist = Averager()
best_epoch = 0 #saves best epoch where loss was minimum
min_loss = sys.maxsize
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
loss_hist.reset()
tk = tqdm(train_data_loader)
for images, targets, image_ids in tk:
images = list(image.to(device) for image in images)
targets = [{k: v.to(device) for k, v in t.items()} for t in targets]
loss_dict = model(images, targets)
losses = sum(loss for loss in loss_dict.values())
loss_value = losses.item()
#send loss value
loss_hist.send(loss_value)
#step up the optimiser and propogate the losses backward
optimizer.zero_grad()
losses.backward()
optimizer.step()
tk.set_postfix(train_loss=loss_value)
tk.close()
# update the learning rate
if lr_scheduler is not None:
lr_scheduler.step()
print(f"Epoch #{epoch} loss: {loss_hist.value}")
# here it saves the model which has mininmum loss.
if loss_hist.value<min_loss:
print("Better model found at epoch {0} with {1:0.5f} loss value".format(epoch,loss_hist.value))
torch.save(model.state_dict(), f"model_state_epoch_{epoch}.pth")
min_loss = loss_hist.value
best_epoch = epoch
# loades the best model at the end of training
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(f"./model_state_epoch_{best_epoch}.pth"));
Validation and Prediction
Below apply_nms function
Performs non-maximum suppression (NMS) on the boxes according to their intersection-over-union (IoU).
NMS iteratively removes lower scoring boxes which have an IoU greater than iou_threshold with another (higher scoring) box.
If multiple boxes have the exact same score and satisfy the IoU criterion with respect to a reference box, the selected box is not guaranteed to be the same between CPU and GPU. This is similar to the behavior of argsort in PyTorch when repeated values are present.
Source : https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/ops.html
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('../input/vinbigdata-abnormalities-detection-imgx512/model_state_epoch_12.pth'));
# the function takes the original prediction and the iou threshold.
def apply_nms(orig_prediction, iou_thresh=0.3):
# torchvision returns the indices of the bboxes to keep
keep = torchvision.ops.nms(orig_prediction['boxes'], orig_prediction['scores'], iou_thresh)
final_prediction = orig_prediction
final_prediction['boxes'] = final_prediction['boxes'][keep]
final_prediction['scores'] = final_prediction['scores'][keep]
final_prediction['labels'] = final_prediction['labels'][keep]
return final_prediction
Let’s take a sample from valid dataset and make Prediction
submission = pd.read_csv('../input/vinbigdata-chest-xray-abnormalities-detection/sample_submission.csv')
ts_ids = submission.image_id.unique().tolist()
TCDS = TestDataset(submission,ts_img_dir2,get_test_transform())
img,_,_,_ = TCDS[0]
test_data_loader = DataLoader(
TCDS,
batch_size=8,
shuffle=False,
num_workers=4,
collate_fn=collate_fn
)
Prediction on Test Set
results = []
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for images, image_ids,_,_ in tqdm(test_data_loader):
images = list(image.to(device) for image in images)
outputs = model(images)
results.append(outputs)
0%| | 0/375 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
img,target,_ = valid_dataset[58]
# put the model in evaluation mode
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
prediction = model([img.to(device)])[0]
print('predicted #boxes: ', len(prediction['labels']))
print('real #boxes: ', len(target['labels']))
predicted #boxes: 94
real #boxes: 1
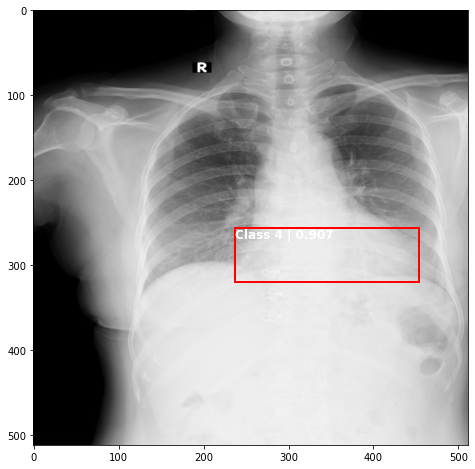
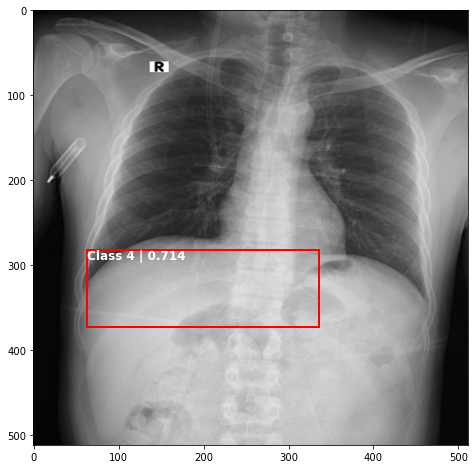
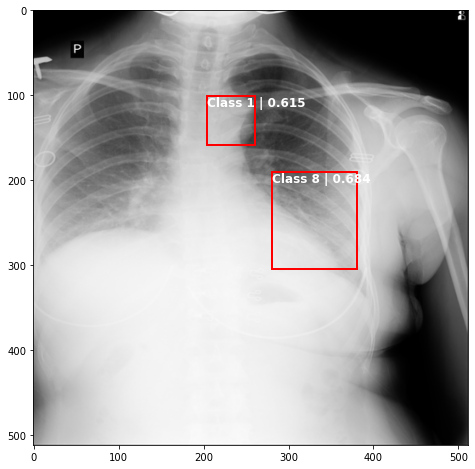
Plotting Predictions
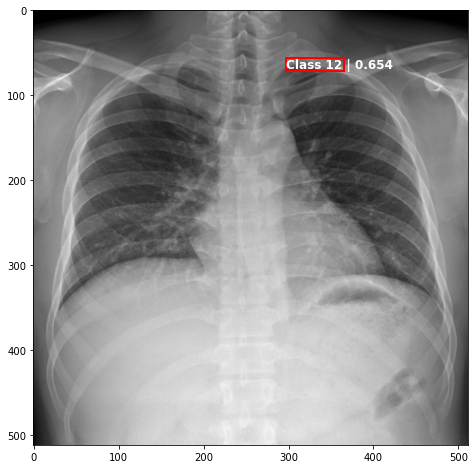
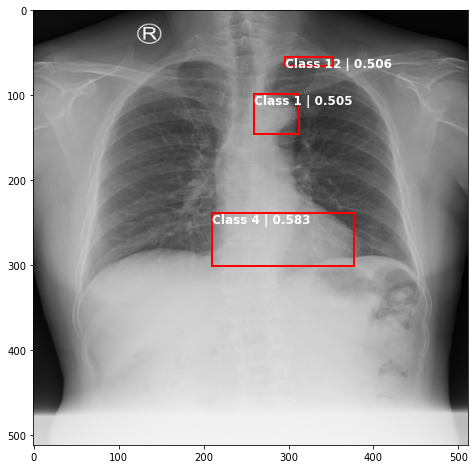
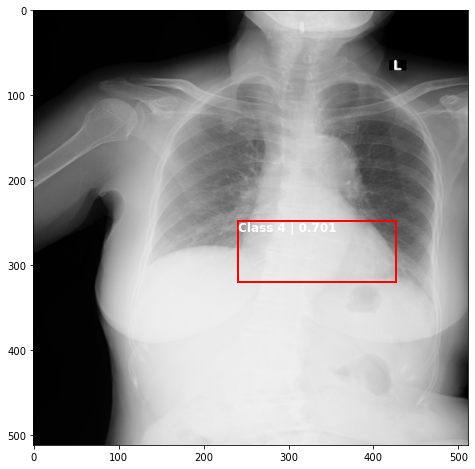
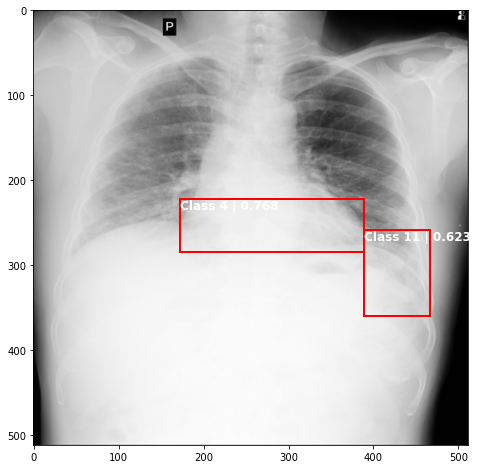
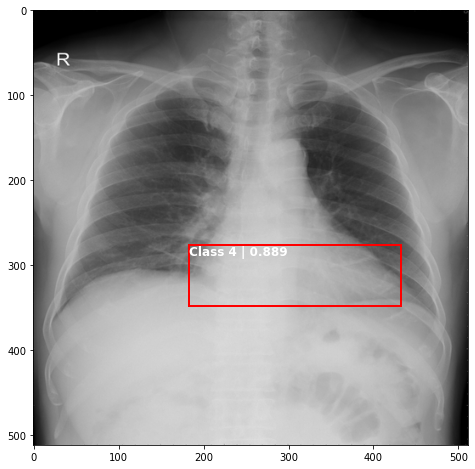
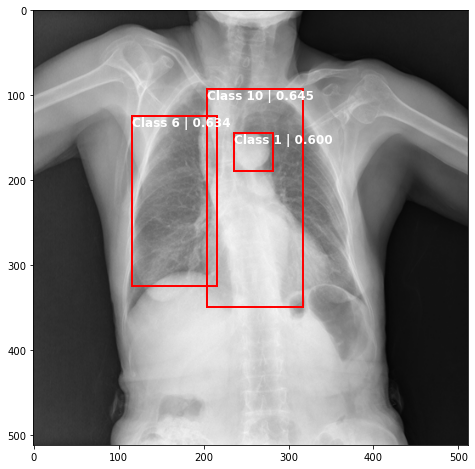
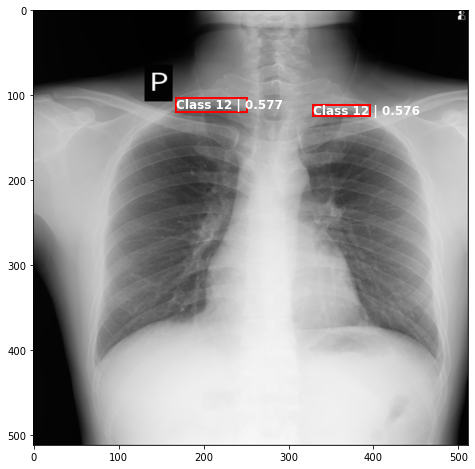
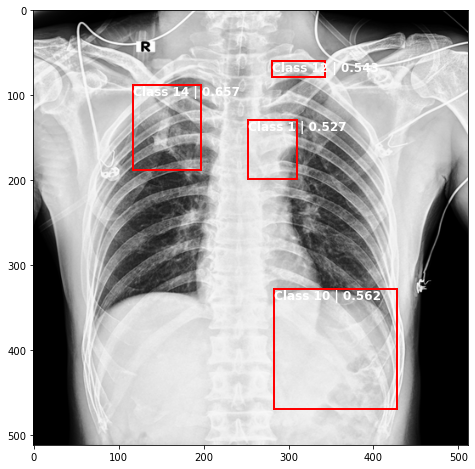
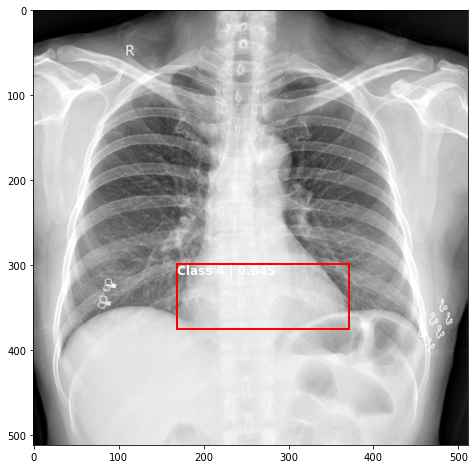
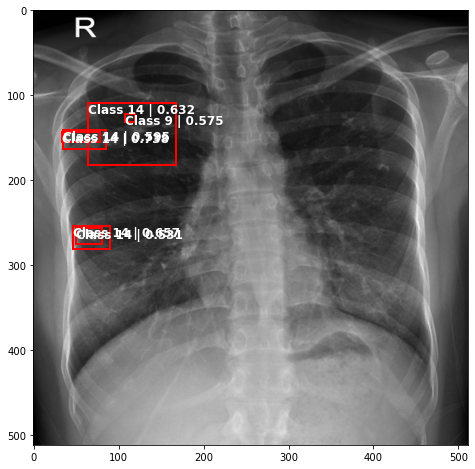
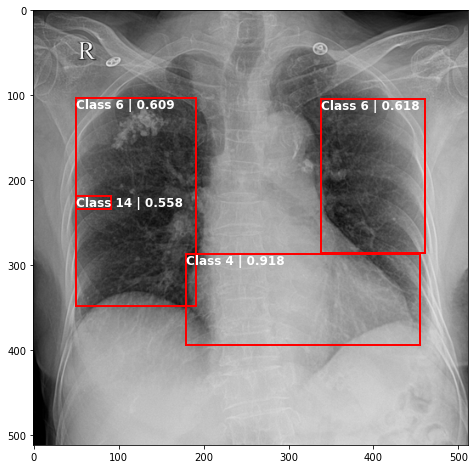
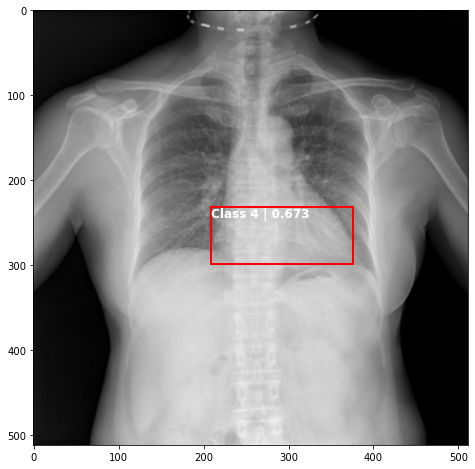
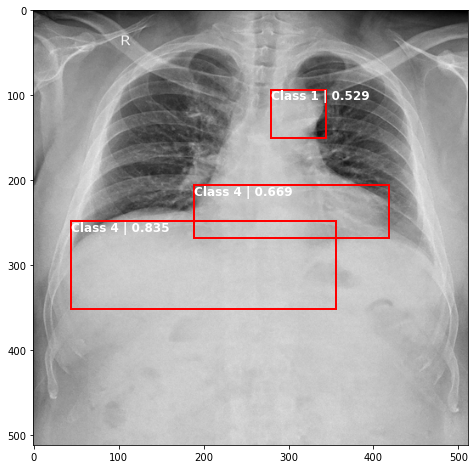
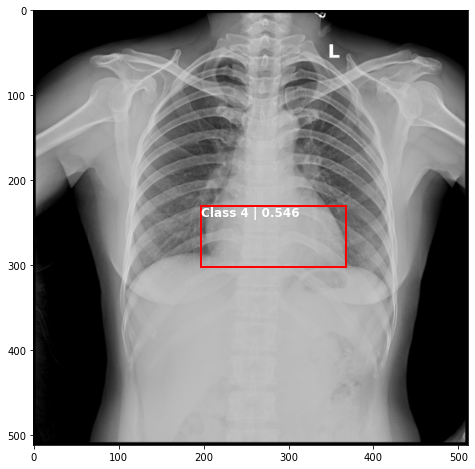
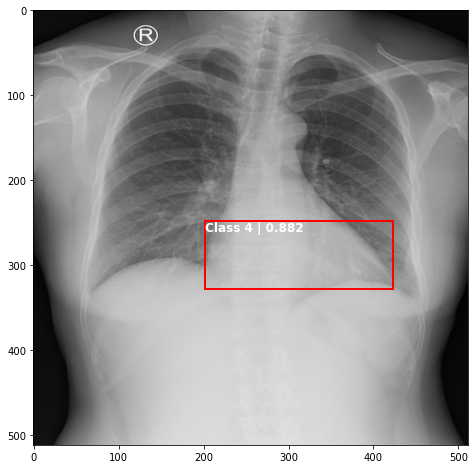
def plot_valid(img,prediction,nms=True,detect_thresh=0.5,iou_thresh=0.2):
'''
img = val_image
nms = use non maximum-supression
prediction dict
detection threshold
intersection over union threshold for non-maximum suppression (NMS)
'''
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,8))
val_img = img.permute(1,2,0).cpu().detach().numpy()
ax.imshow(val_img)
nms_prediction = apply_nms(prediction, iou_thresh=iou_thresh) if nms else prediction
val_scores = nms_prediction['scores'].cpu().detach().numpy()
bbox = nms_prediction['boxes'].cpu().detach().numpy()
lbls = nms_prediction['labels'].cpu().detach().numpy()
for i in range(len(bbox)):
if val_scores[i]>=detect_thresh:
box = bbox[i]
x,y,w,h = box[0], box[1], box[2]-box[0], box[3]-box[1]
rect = matplotlib.patches.Rectangle((x,y),w,h,linewidth=2,edgecolor='r',facecolor='none',)
ax.text(*box[:2], "Class {0} | {1:.3f}".format(lbls[i],val_scores[i]), verticalalignment='top', color='white', fontsize=12, weight='bold')
ax.add_patch(rect)
plt.show()
plot_valid(img,prediction,False)
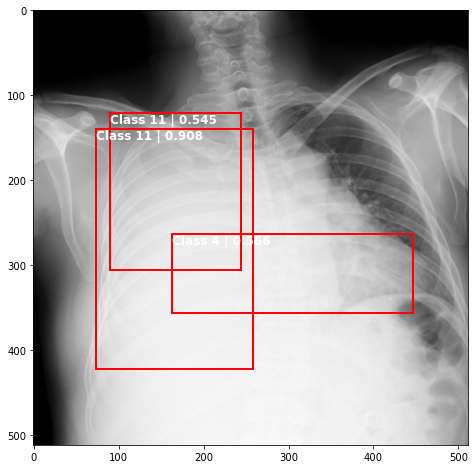
j = -1
for i in range(20):
if i%8==0:
j+=1
ts_img,_,_,_ = TCDS[i]
plot_valid(ts_img,results[j][i%8],False)