Duplicate Question Classification Bert
Question Semantic similarity
- Finding How similar two questions are ; Classifing are they duplicate
Helpful Downloads and Installation
Below is fork of abhishek thakur’s
- Tez is fast pytorch trainer, it helps in training pytorch code. With support for fp16 training, callbacks, load and save models.
- Still keeping your models pretty close to pytorch.
!git clone https://github.com/shadab4150/tez.git
Cloning into 'tez'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 320, done.[K
remote: Counting objects: 100% (320/320), done.[K
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (224/224), done.[K
remote: Total 320 (delta 164), reused 218 (delta 75), pack-reused 0[K
Receiving objects: 100% (320/320), 56.20 KiB | 11.24 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (164/164), done.
tez_path = '/content/tez/'
import sys
sys.path.append(tez_path)
from google.colab import files
uploaded = files.upload()
for fn in uploaded.keys():
print('User uploaded file "{name}" with length {length} bytes'.format(name=fn, length=len(uploaded[fn])))
# Then move kaggle.json into the folder where the API expects to find it.
!mkdir -p ~/.kaggle/ && mv kaggle.json ~/.kaggle/ && chmod 600 ~/.kaggle/kaggle.json
Saving kaggle.json to kaggle.json
User uploaded file "kaggle.json" with length 74 bytes
!pip uninstall kaggle -y
!pip install -qq kaggle
Uninstalling kaggle-1.5.10:
Successfully uninstalled kaggle-1.5.10
[K |████████████████████████████████| 61kB 8.1MB/s
[?25h Building wheel for kaggle (setup.py) ... [?25l[?25hdone
Download dataset from kaggle
!kaggle competitions download -c quora-question-pairs
Downloading quora-question-pairs.zip to /content
96% 297M/309M [00:02<00:00, 144MB/s]
100% 309M/309M [00:02<00:00, 131MB/s]
Unzip it
!unzip '/content/quora-question-pairs.zip'
!unzip '/content/train.csv.zip'
!unzip '/content/test.csv.zip'
Archive: /content/quora-question-pairs.zip
inflating: sample_submission.csv.zip
inflating: test.csv
inflating: test.csv.zip
inflating: train.csv.zip
Archive: /content/train.csv.zip
inflating: train.csv
Archive: /content/test.csv.zip
replace test.csv? [y]es, [n]o, [A]ll, [N]one, [r]ename: y
inflating: test.csv
Install Transformers library
!pip install -qq transformers
[K |████████████████████████████████| 1.8MB 15.8MB/s
[K |████████████████████████████████| 890kB 58.4MB/s
[K |████████████████████████████████| 3.2MB 56.2MB/s
[?25h Building wheel for sacremoses (setup.py) ... [?25l[?25hdone
Importing Libraries
import tez
import transformers
import torch
import sys
import torch.nn as nn
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import sklearn
from pathlib import Path
Loading Dataset
trn_df = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
path = Path('/content')
trn_df.sample(n=5)
| id | qid1 | qid2 | question1 | question2 | is_duplicate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 135793 | 135793 | 216794 | 216795 | Why CS, being professional course in India, is... | What would be it's value in Indian market if I... | 0 |
| 395498 | 395498 | 528490 | 528491 | What kind of work people do from ECE backgroun... | What is the experience like working as an engi... | 0 |
| 37287 | 37287 | 67866 | 67028 | How can we read people's mind? | How can I read a human mind? | 1 |
| 279202 | 279202 | 398594 | 398595 | Which are websites which offer Free online cer... | What makes the AR15 such a popular rifle? | 0 |
| 249680 | 249680 | 58494 | 298813 | Which are some of the biggest mistakes you hav... | What is the biggest mistake you have done in y... | 1 |
trn_df.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 404290 entries, 0 to 404289
Data columns (total 6 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 id 404290 non-null int64
1 qid1 404290 non-null int64
2 qid2 404290 non-null int64
3 question1 404289 non-null object
4 question2 404288 non-null object
5 is_duplicate 404290 non-null int64
dtypes: int64(4), object(2)
memory usage: 18.5+ MB
Stratified KFOLD
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
trn_df['kfold'] = -1
trn_df = trn_df.sample(frac=1.)
y = trn_df['is_duplicate'].values
skf = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=20)
for fld, (trn_,val_) in enumerate(skf.split(X=trn_df,y=y)):
trn_df.loc[val_,'kfold'] = fld
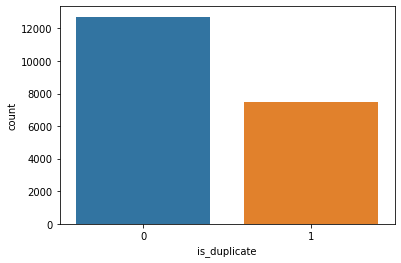
sns.countplot(x=trn_df[trn_df.kfold==1].is_duplicate);
Cleaning the Text
A function that cleans the text, with options to remove stopwords as well as stem words.
import re
import nltk
nltk.download('stopwords')
STOPWORDS = nltk.corpus.stopwords.words('english')
def text_to_wordlist(text, remove_stopwords=False, stem_words=False):
# Clean the text, with the option to remove stopwords and to stem words.
# Convert words to lower case and split them
text = text.lower().split()
# Optionally, remove stop words
if remove_stopwords:
text = [w for w in text if not w in STOPWORDS]
text = " ".join(text)
# Remove punctuation from text
# text = "".join([c for c in text if c not in punctuation])
# Clean the text
text = re.sub(r"[^A-Za-z0-9^,!.\/'+-=]", " ", text)
text = re.sub(r"what's", "what is ", text)
text = re.sub(r"\'s", " ", text)
text = re.sub(r"\'ve", " have ", text)
text = re.sub(r"can't", "cannot ", text)
text = re.sub(r"n't", " not ", text)
text = re.sub(r"i'm", "i am ", text)
text = re.sub(r"\'re", " are ", text)
text = re.sub(r"\'d", " would ", text)
text = re.sub(r"\'ll", " will ", text)
text = re.sub(r",", " ", text)
text = re.sub(r"\.", " ", text)
text = re.sub(r"!", " ! ", text)
text = re.sub(r"\/", " ", text)
text = re.sub(r"\^", " ^ ", text)
text = re.sub(r"\+", " + ", text)
text = re.sub(r"\-", " - ", text)
text = re.sub(r"\=", " = ", text)
text = re.sub(r"'", " ", text)
text = re.sub(r":", " : ", text)
text = re.sub(r"(\d+)(k)", r"\g<1>000", text)
text = re.sub(r" e g ", " eg ", text)
text = re.sub(r" b g ", " bg ", text)
text = re.sub(r" u s ", " american ", text)
# text = re.sub(r"\0s", "0", text) # It doesn't make sense to me
text = re.sub(r" 9 11 ", "911", text)
text = re.sub(r"e - mail", "email", text)
text = re.sub(r"j k", "jk", text)
text = re.sub(r"\s{2,}", " ", text)
# Optionally, shorten words to their stems
if stem_words:
text = text.split()
stemmer = SnowballStemmer('english')
stemmed_words = [stemmer.stem(word) for word in text]
text = " ".join(stemmed_words)
# Return a list of words
return(text)
[nltk_data] Downloading package stopwords to /root/nltk_data...
[nltk_data] Package stopwords is already up-to-date!
Split it into train and valid dataframe
val_df = trn_df[trn_df.kfold==3].copy() # valid
train_df = trn_df[trn_df.kfold<3].copy() # train
ts_df = trn_df[trn_df.kfold==8].copy() # test
train_df.shape,val_df.shape
((60645, 7), (20215, 7))
Clean the text
train_df['question1'] = train_df['question1'].apply(lambda x: text_to_wordlist(str(x), remove_stopwords=False))
train_df['question2'] = train_df['question2'].apply(lambda x: text_to_wordlist(str(x), remove_stopwords=False))
val_df['question1'] = val_df['question1'].apply(lambda x: text_to_wordlist(str(x), remove_stopwords=False))
val_df['question2'] = val_df['question2'].apply(lambda x: text_to_wordlist(str(x), remove_stopwords=False))
train_df.head()
| id | qid1 | qid2 | question1 | question2 | is_duplicate | kfold | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 588 | 588 | 1174 | 1175 | How do I work with machine learning researcher... | How can undergraduate help with machine learni... | 0 | 0 |
| 22456 | 22456 | 17746 | 14730 | How do i get started on machine learning? | What are some good books or references to get ... | 1 | 1 |
| 54175 | 54175 | 94845 | 95667 | How do I become an expert coder? | What should be the stratergy to be a great coder? | 1 | 2 |
| 31707 | 31707 | 58439 | 58440 | What is called simple living style? | What is the mantra to live a simple life? | 0 | 1 |
| 37295 | 37295 | 37964 | 67879 | How can I stop myself from spending more time ... | How can I stop myself from wasting time on the... | 1 | 1 |
Preparing Dataset and DataLoader for text data
from transformers import AdamW,get_linear_schedule_with_warmup
import sklearn.metrics as sklm
Transformers take text, or text pairs. and returns.
-
inputs_ids : The input ids are often the only required parameters to be passed to the model as input. They are token indices, numerical representations of tokens building the sequences that will be used as input by the model.
-
attention_mask : The attention mask is an optional argument used when batching sequences together. This argument indicates to the model which tokens should be attended to, and which should not.
-
token_type_ids : Some models’ purpose is to do sequence classification or question answering. These require two different sequences to be joined in a single “input_ids” entry, which usually is performed with the help of special tokens, such as the classifier ([CLS]) and separator ([SEP]) tokens.
https://huggingface.co/transformers/main_classes/tokenizer.html
class BERTDataset:
def __init__(self, texts1,texts2, targets,max_len=64):
#Question 1st
self.texts1 = texts1
# Question 2nd
self.texts2 = texts2
# target is duplicate
self.targets = targets
# tokenizer from transformers
self.tokenizer = transformers.BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(
"bert-base-cased",
do_lower_case=False
)
self.max_len = max_len
def __len__(self):
return min(len(self.texts1),len(self.texts2))
def __getitem__(self,idx):
text1 = str(self.texts1[idx])
text2 = str(self.texts2[idx])
# a simple text split and join to clean
text1 = " ".join(text1.split())
text2 = " ".join(text2.split())
# tokenize
inputs = self.tokenizer.encode_plus(
text1,
text2,
add_special_tokens=True,
max_length=self.max_len,
padding="max_length",
truncation=True
)
# return from dataset
#After tokenizing, bert excepts input_ids for text, there mask as well token type ids.
resp = {
"ids" : torch.tensor(inputs["input_ids"],dtype=torch.long),
"mask" : torch.tensor(inputs["attention_mask"],dtype=torch.long),
"token_type_ids" : torch.tensor(inputs["token_type_ids"],dtype=torch.long),
"targets" : torch.tensor(self.targets[idx],dtype=torch.float)
}
return resp
Train and valid set
train_dataset = BERTDataset(train_df.question1.values,train_df.question2.values,train_df.is_duplicate.values)
valid_dataset = BERTDataset(val_df.question1.values,val_df.question2.values,val_df.is_duplicate.values)
Test Dataset
test_dataset = BERTDataset(ts_df.question1.values,ts_df.question2.values,ts_df.is_duplicate.values)
train_dataset[0]
{'ids': tensor([ 101, 1731, 1202, 146, 1250, 1114, 3395, 3776, 6962, 1170, 7477, 136,
102, 1731, 1169, 8448, 1494, 1114, 3395, 3776, 1844, 136, 102, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0]),
'mask': tensor([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]),
'targets': tensor(0.),
'token_type_ids': tensor([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])}
Question Similarity Model
class QuestionModel(tez.Model):
def __init__(self,num_classes,num_train_steps):
super().__init__()
# Load Bert Pretrained Model
self.bert = transformers.BertModel.from_pretrained(
"bert-base-cased",return_dict=False)
# A Dropout Before final Output
self.bert_drop = nn.Dropout(0.3)
# Final layer out.
self.out = nn.Linear(768,num_classes)
self.num_train_steps = num_train_steps
self.step_scheduler_after = "batch"
def fetch_optimizer(self):
# optimiser
opt = AdamW(self.parameters(),lr=1e-4)
return opt
def fetch_scheduler(self):
# learning rate scheduler
sch = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup(
self.optimizer,num_warmup_steps=0,num_training_steps=self.num_train_steps
)
return sch
def loss(self,outputs,targets):
# loss function
if targets is None:
return None
return nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(outputs, targets.view(-1,1))
def monitor_metrics(self,outputs,targets):
#metrics to monitor model performance
if targets is None:
return {}
outputs = torch.sigmoid(outputs).cpu().detach().numpy()
targets = targets.cpu().detach().numpy()
acc = sklm.accuracy_score(targets,outputs>=0.5)
try:
score1 = sklm.roc_auc_score(targets, outputs)
score2 = sklm.log_loss(targets, outputs)
except:
score1 = 0.5
score2 = 0.5
return {"roc_auc": score1,"accuracy":acc}
def forward(self,ids,mask,token_type_ids,targets=None):
# model input and output
_,x1 = self.bert(ids,attention_mask=mask,token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
x = self.bert_drop(x1)
x = self.out(x)
if targets is not None:
loss = self.loss(x,targets)
met = self.monitor_metrics(x,targets)
return x, loss, met
return x,-1, {}
TRAIN_BS = 16 # train batch size
EPOCHS = 10 # number of epochs to train
n_train_steps = int(len(train_df) / TRAIN_BS* EPOCHS);n_train_steps
37903
Model
model = QuestionModel(num_classes=1,num_train_steps=n_train_steps)
Callbacks:
- Early stopping callback, to regularize the model
es = tez.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor="valid_accuracy", model_path="model.bin")
Training
model.fit(train_dataset,
valid_dataset=valid_dataset,
device="cuda",
epochs=2,
callbacks=[es],
train_bs=32,
fp16=True)
HBox(children=(FloatProgress(value=0.0, max=1896.0), HTML(value='')))
HBox(children=(FloatProgress(value=0.0, max=1264.0), HTML(value='')))
Validation score improved (inf --> 0.814725079113924). Saving model!
HBox(children=(FloatProgress(value=0.0, max=1896.0), HTML(value='')))
HBox(children=(FloatProgress(value=0.0, max=1264.0), HTML(value='')))
EarlyStopping counter: 1 out of 5
Predicting test set
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
preds = model.predict(test_dataset, batch_size=64, n_jobs=-1, device="cuda")
y_pred = []
for p in tqdm(preds):
y_pred += list(p.flatten())
y_pred = torch.sigmoid(torch.tensor(y_pred)).numpy()
HBox(children=(FloatProgress(value=1.0, bar_style='info', max=1.0), HTML(value='')))
HBox(children=(FloatProgress(value=0.0, max=316.0), HTML(value='')))
accuracy score test set
sklm.accuracy_score(ts_df.is_duplicate.values,y_pred>=0.5)
0.8256245362354687
Fine tuning for just 2 epochs and we got 82.56% accuracy
import gc
model = None
gc.collect()
3390